Cyclic Variations In The Occurrence Of Disease May Reflect:
Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect:. True Descriptive epidemiology characterizes the amount and distribution of disease within a population and enables the researcher to. Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect. Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect.
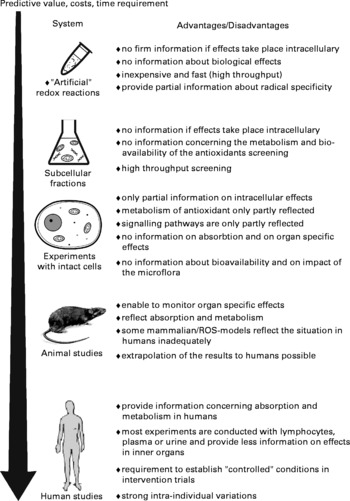
Changes in the risk-taking behavior of persons Correct Answers. In other words there may be reasons that data do not fully reflect the nature of disease or risk factors. 2 evaluate past temporal trends and assess whether such trends are still occurring.
Each acute infectious disease has its own seasonal window of occurrence which importantly may vary among geographic locations and differ from other diseases within the same location. We assessed the temporal and racial variations in heart defect occurrence during a 30-year period in a well-defined population. Our objectives were to.
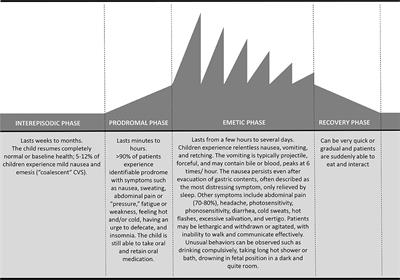
Contact with a disease-causing factor or the amount of the factor that affects a group of individuals Epi data are AT BEST approximations of what is occurring in the real world. Cyclic Cushings syndrome CS involves rhythmic fluctuations in ACTH secretion resulting in a cyclic variation of adrenal steroid production. Changes in exposure to infectious agents Changes in the risk-taking behavior of persons Changes in temporary stressors Endogenous biologic factors All of the above 2 An epidemiologic survey of roller-skating injuries in Metroville a city with a population of.
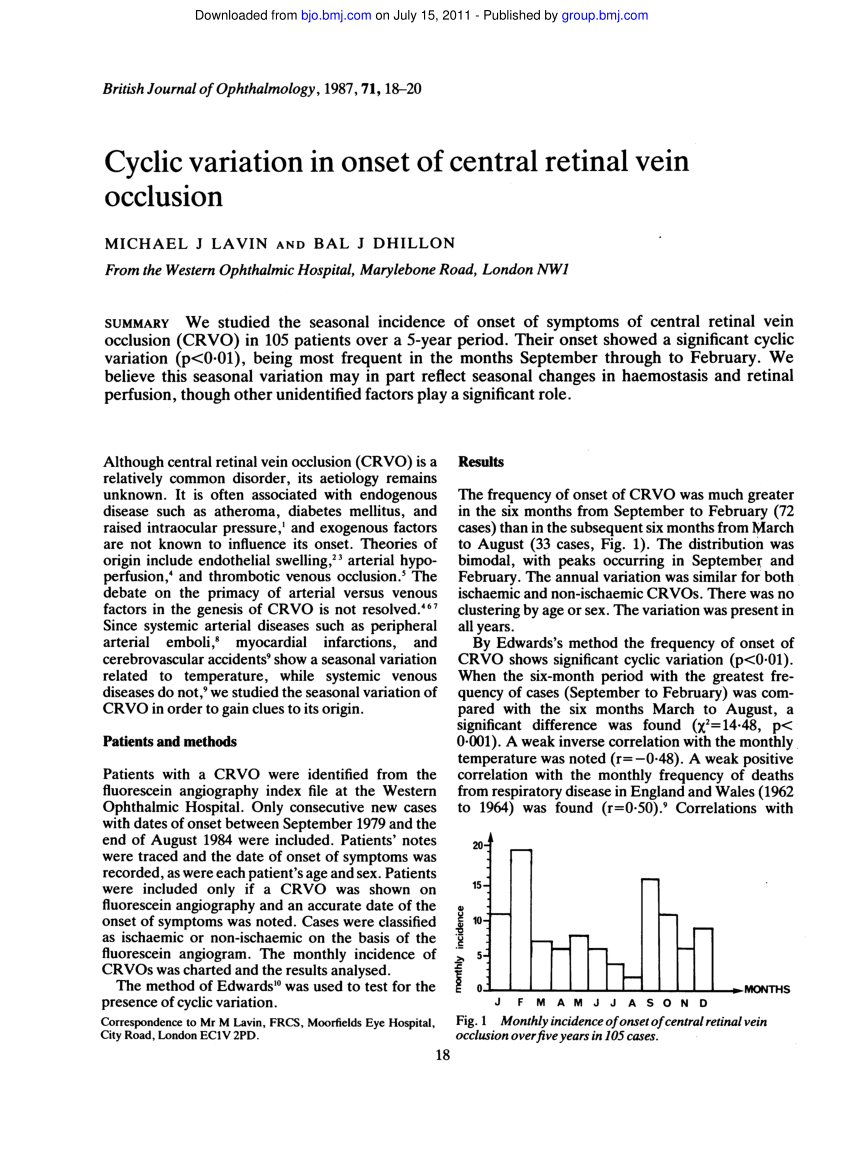
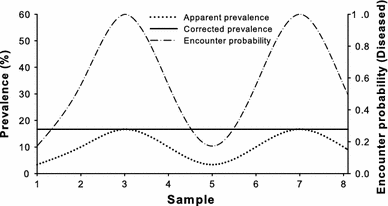
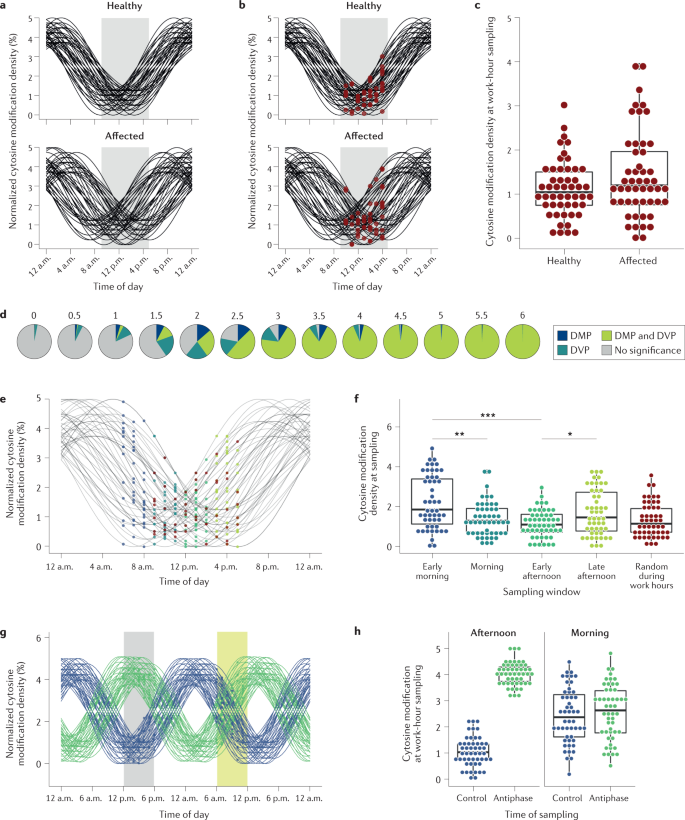
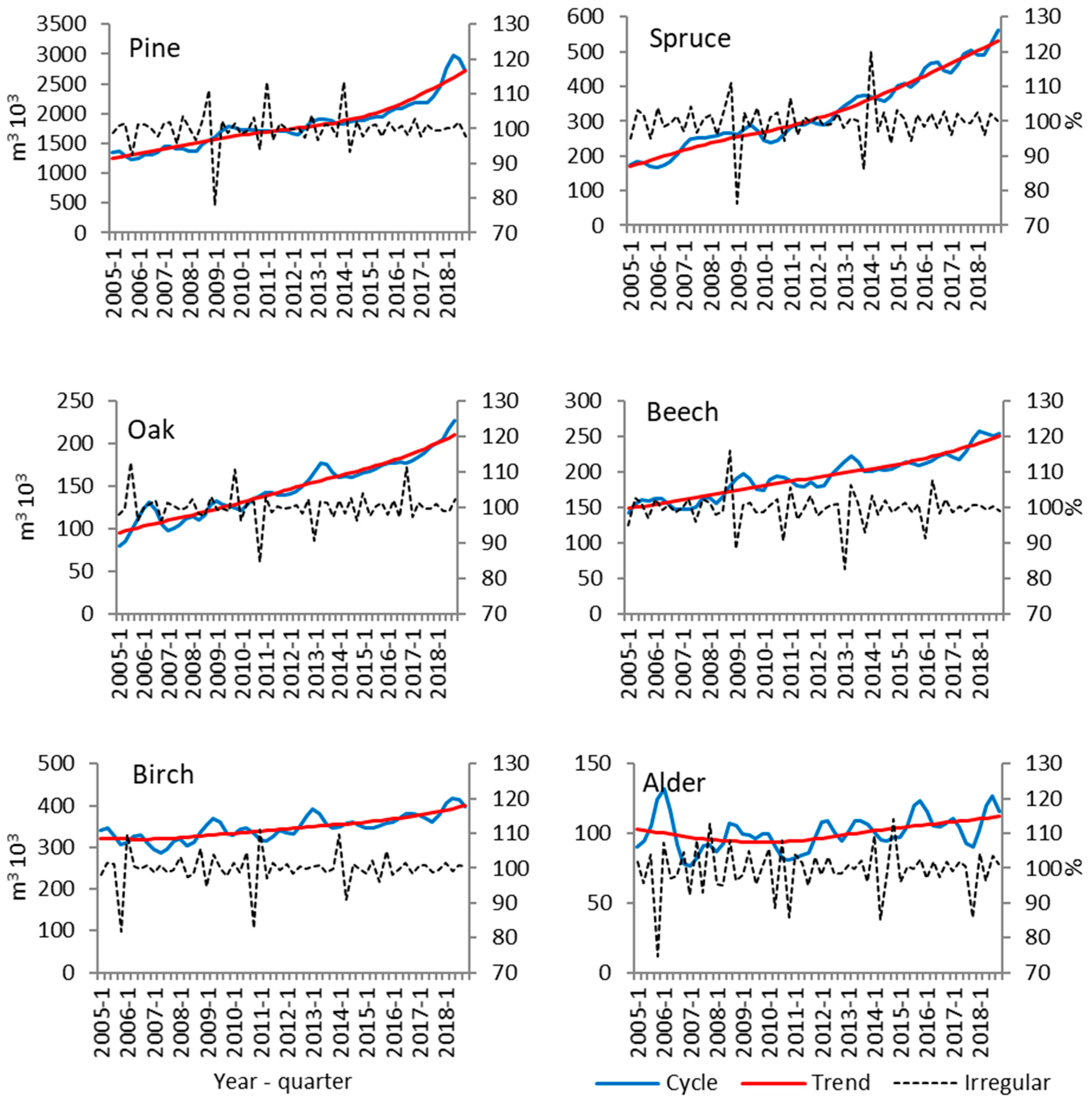
Health phenomena may show cyclic variations in a persons response to temporary stressors. In the majority of cases cyclic CS is caused by an ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma but it can also be due to ectopic ACTH production or an adrenal adenoma. Seasonal cyclicity is a ubiquitous feature of acute infectious diseases and may be a ubiquitous feature of human infectious diseases in general as illustrated in Tables 14.
And 3 assess whether such trends differed by race. Seasonal variation in transmission tends to reduce disease persistence due to the low number of cases between epidemic peaks and the possibility of stochastic extinction of infection. Variations in mortality between Western and Asian-Pacific countries may result from differences in disease detection or management and variations in gender predilection peak age of onset frequency of concurrent immune diseases and serological profile may reflect gender-biased and age-related antigen exposures and genetic predispositions.
Chapters 3 4 Quiz 1 Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect. Seasonal variations in cases of influenza and the fact that influenza is a disappearing disorder.
Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect.
1 provide a more recent estimate of the impact of major heart defects than is currently available. The prevalence of the disease. Seasonal cyclicity is a ubiquitous feature of acute infectious diseases and may be a ubiquitous feature of human infectious diseases in general as illustrated in Tables 14. The importance of stochastic extinction or fade-out has long been recognized with Bartlett 1957 first drawing attention to an apparent critical community size for measles below which stochastic fade-out. Chapters 3 4 Quiz 1 Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect. Changes in exposure to infectious agents Changes in the risk-taking behavior of persons Changes in temporary stressors Question 5 Successful treatment programs that would shorten the duration of a disease. Cyclic Cushings syndrome CS involves rhythmic fluctuations in ACTH secretion resulting in a cyclic variation of adrenal steroid production. Cyclic variations in the occurrence of pneumonia and influenza mortality may reflect. 2 evaluate past temporal trends and assess whether such trends are still occurring.
Changes in exposure to infectious agents Changes in the risk-taking behavior of persons Changes in temporary stressors Question 5 Successful treatment programs that would shorten the duration of a disease. Cyclic Cushings syndrome CS involves rhythmic fluctuations in ACTH secretion resulting in a cyclic variation of adrenal steroid production. Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect. Variations in mortality between Western and Asian-Pacific countries may result from differences in disease detection or management and variations in gender predilection peak age of onset frequency of concurrent immune diseases and serological profile may reflect gender-biased and age-related antigen exposures and genetic predispositions. Chapters 3 4 Quiz 1 Cyclic variations in the occurrence of disease may reflect. Our objectives were to. Changes in exposure to infectious agents Changes in the risk-taking behavior of persons Changes in temporary stressors Question 5 Successful treatment programs that would shorten the duration of a disease.

























Post a Comment for "Cyclic Variations In The Occurrence Of Disease May Reflect:"