Acute Kidney Injury Superimposed On Chronic Kidney Disease
Acute kidney injury superimposed on chronic kidney disease. Previous conventional wisdom suggested patients who survived an episode of acute kidney injury AKI fully recovered renal function. Star MD and Paul L. Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease N17-N19.
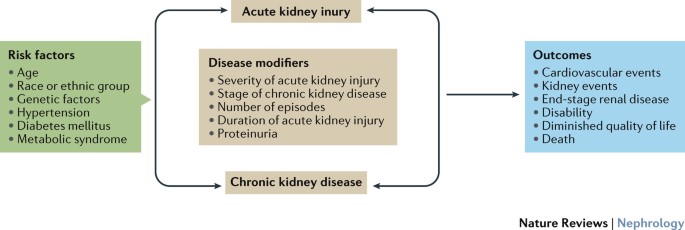
However when the repair is more severe or is superimposed on baseline kidney abnormalities the repair process can lead to fibrosis which can facilitate progression to chronic kidney disease. There is increasing recognition that acute kidney injury AKI and chronic kidney disease CKD are closely linked and likely promote one another. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease.
Come analysis studies have brought to our attention the important role played by acute kidney injury AKI in the progression of chronic kidney disease CKD to end-stage renal disease ESRD. The first focus of primary care is to prevent acute-on-chronic kidney disease from occurring. However the expression and performance of AKI biomarkers in acute injury superimposed on preexisting CKD AonC.
A type 2 excludes note represents not included here. An integrated clinical syndrome. However preventative strategies cannot remove the risk completely.
Acute kidney injury should be considered a medical emergency. AKI can cause end-stage renal disease ESRD directly and increase the risk of developing incident chronic kidney. AKI accelerates progression in patients with CKD.
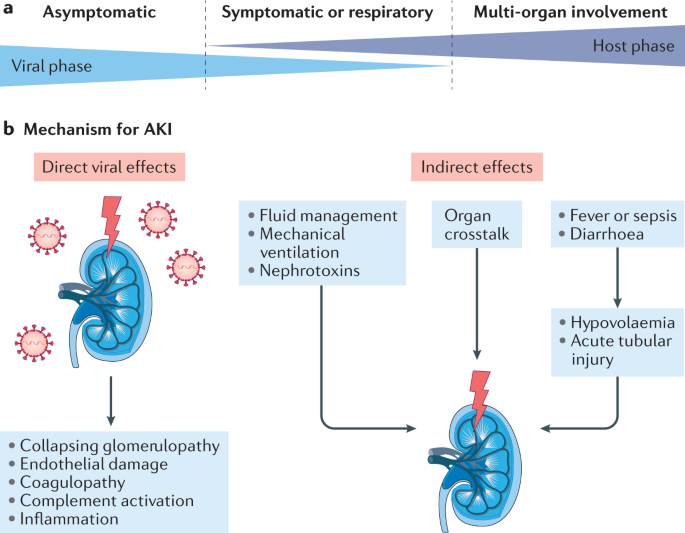
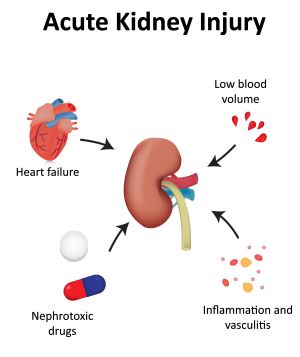
Acute kidney injury AKI formerly called acute kidney failure is a sudden decline in glomerular filtration rate GFR. AKI can cause end-stage renal disease ESRD directly and increase the risk of developing incident chronic kidney disease CKD and worsening of underlying CKD. 17 patients needed acute haemodialysis.
Underlying CKD is now recognized as a clear risk factor for AKI as both decreased glomerular filtration rate GFR and increased proteinuria have each been shown to be strongly associated with AKI. Acute kidney injury in a community setting occurs most commonly in people with existing chronic kidney disease.
Acute kidney injury in a community setting occurs most commonly in people with existing chronic kidney disease.
Acute kidney injury AKI formerly called acute kidney failure is a sudden decline in glomerular filtration rate GFR. A multicenter prospective study. Epidemiological studies now show that patients who have had acute kidney injury have a marked increase in their risk for the development of end-stage renal disease. This review considers evidence that acute and chronic kidney diseases are not distinct entities but rather are closely interconnected. Acute kidney injury AKI formerly called acute kidney failure is a sudden decline in glomerular filtration rate GFR. AKI can cause end-stage renal disease ESRD directly and increase the risk of developing incident chronic kidney. The first focus of primary care is to prevent acute-on-chronic kidney disease from occurring. Come analysis studies have brought to our attention the important role played by acute kidney injury AKI in the progression of chronic kidney disease CKD to end-stage renal disease ESRD. Chronic kidney disease CKD is a risk factor for the development of acute kidney injury AKI.
Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in acute kidney injury superimposed on chronic kidney disease after cardiac surgery. The previous conventional wisdom that survivors of acute kidney injury AKI tend to do well and fully recover renal function appears to be flawed. A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. Chronic kidney disease CKD is a risk factor for the development of acute kidney injury AKI. Acute kidney injury AKI formerly called acute kidney failure is a sudden decline in glomerular filtration rate GFR. Acute kidney injury AKI is a common disorder with a population incidence of about 2000 per million population pmp. Epidemiological studies now show that patients who have had acute kidney injury have a marked increase in their risk for the development of end-stage renal disease.
































Post a Comment for "Acute Kidney Injury Superimposed On Chronic Kidney Disease"